O-rings are elastomeric and donut-shaped gaskets designed to create fluid-tight seals between mated parts within a fluid system. Although simplistic in design and function, these components perform a critical role. When used correctly in fluid handling and processing systems, they ensure process liquids and gases remain inside the proper areas and potential contaminants stay outside of sensitive areas. Some of the typical industries that regularly make use of O-rings include transportation, medical, electronics, oil and gas, and food and beverage.
The following article provides a comprehensive overview of O-rings—including their design considerations, types available, materials used, manufacturing processes, and industrial applications—to aid in proper selection.
What Are O-Rings?
By technical definition, all O-rings can be considered gaskets, but not all gaskets can be regarded as O-rings. Although both create seals that prevent fluids from leaking in or out of the area between two mated components, there are critical differences in their design and performance. One of the primary distinctions between the two is the shape of flange they accommodate; gaskets require flanges with flat surfaces, while O-rings need ones with a channel or groove. For the latter, this design element helps avoid blowout in high-pressure environments in which other gaskets would likely fail.
When properly sized and compressed within the groove between two mated components, O-rings form tight seals that prevent the escape of gases and liquids. They are available in several variations to suit the needs of a wide range of applications.
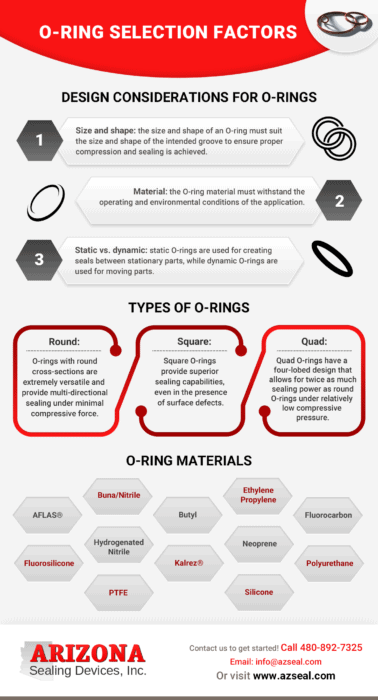
Design Considerations for O-Rings
When choosing an O-ring for an application, the following design elements should be considered:
- Size and shape: the size and shape of an O-ring must suit the size and shape of the intended groove to ensure proper compression and sealing is achieved
- Material: the O-ring material must withstand the operating and environmental conditions of the application
- Static vs. dynamic: static O-rings are used for creating seals between stationary parts, while dynamic O-rings are used for moving parts
Types of O-Rings
As indicated above, many design factors affect the sealing performance of an O-ring. Some of the common types of O-rings available and their applications include:
- Round: O-rings with round cross-sections are extremely versatile and provide multi-directional sealing under minimal compressive force.
- Square: Square O-rings provide superior sealing capabilities, even in the presence of surface defects.
- Quad: Quad O-rings have a four-lobed design that allows for twice as much sealing power as round O-rings under relatively low compressive pressure.
Common O-Ring Materials
The type of material used to create an O-ring significantly influences its ability to perform reliably when used in the intended application. Typical elastomeric materials used in the construction of O-rings include:
- AFLAS®
- Buna/Nitrile
- Butyl
- Ethylene Propylene
- Fluorocarbon
- Fluorosilicone
- Hydrogenated Nitrile
- Kalrez®
- Neoprene
- Polyurethane
- PTFE
- Silicone
When selecting a material for an O-ring, there are several considerations to keep in mind, such as:
- Gland type and fill: The opening (gland) into which the O-ring is installed must allow for the appropriate level of compression and gland fill percentage to avoid O-ring failure.
- Stretch: The material should exhibit the appropriate amount of circumferential stretching to fit properly within the groove
- Compression squeeze: The material should maintain an appropriate level of compression squeeze (deformation) under the expected pressure level.
- Industry standards: Some industries require the use of materials that exhibit specific properties, such as food-grade or military-grade.
To learn more about selecting the right o-ring material for your application, read our o-ring materials guide.
How Are O-Rings Made?
The manufacturing technique used to create an O-ring largely depends on the material employed and the performance level required. The most common O-ring production methods include:
- Compression molding: The material is placed into and enclosed within an open heated mold cavity, compressing and shaping it into the O-ring shape.
- Transfer molding: The material is placed under intense pressure, forcing it into a mold cavity of the O-ring shape.
- Injection molding: The material is heated and injected into the cavity of a mold. Once cooled, it maintains the desired O-ring shape.
- Extrusion: The material is heated and forced through a die with an opening that forms it into the desired O-ring shape as it exits.
Applications of O-Rings
When selected and used properly, O-rings form fluid-tight seals in a wide range of equipment and systems, even when exposed to high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. Some examples of typical use cases include:
- Static axial systems: In static axial systems, the O-ring design should consider the pressure direction (inward or outward) as it affects the inner and outer groove diameters and widths required for optimal sealing.
- Reciprocating dynamic systems: In reciprocating hydraulic or pneumatic systems, the diameter of the O-ring depends on whether the O-ring is used for short stroke applications (smaller diameter preferred) or long-stroke applications (thicker cross sections preferred).
- Rotary systems: O-rings can function as reliable rotary shaft seals under the right conditions, but the correct O-ring compound for the application’s speed (feet per minute) must be selected.
The versatility of O-rings makes them well-suited for use in a diverse set of industries, such as:
- Chemical processing
- Electronics
- Energy
- Fluid power
- Food and beverage
- Medical
- Oil and gas
- Transportation
- Water systems
O-Ring Seals from Arizona Sealing Devices
Founded in 1989, Arizona Sealing Devices is a distributor of high-quality standard and specialized sealing products. Equipped with over three decades of industry experience and an ever-expanding product selection, we can ensure that each O-ring variable (shape, size, material, etc.) and its compatibility with the operating system is carefully considered when choosing a sealing solution.
We offer an extensive O-ring catalog, which encompasses a variety of material compounds and durometers, sizes (for inner, outer, and cross-sectional diameters), performance characteristics, and industry compliances (e.g., Mil-spec, food-grade, and metric). As an ISO 9001:2015 and AS9120B certified company, we guarantee the delivery of a quality and dependable product solution that meets all relevant regulatory requirements and satisfies your sealing needs.
For additional information on O-rings or assistance choosing one for your unique application, contact us today.