Selecting the appropriate O-ring size is crucial for forming effective and reliable seals in both static and dynamic applications. If the dimensions are incorrect, leaks can occur, the sealing system may fail prematurely, or it may be too difficult to install the O-ring. To mitigate these risks, engineers and maintenance professionals rely on sizing charts that specify standard measurements. This makes it easier to verify that the specified size is ordered and installed during manufacturing and maintenance.
O-rings can be measured in standard (i.e., inch) or metric (i.e., millimeter) units. In the US, many manufacturers work with AS568 standard sizes, though additional measurement standards include ISO, British, Japanese, German, French, and Swedish.
How to Measure an O-Ring
Standard (i.e., AS568) O-ring sizing charts list common sizes based on both inside diameter (ID) and cross-section diameter (CS). Each combination of ID and CS is given a unique identification number. Once you have the ID and CS measurements, you can select the corresponding size on the chart below. For example, a size AS568-001 0-ring has an ID of .029±.004” and CS of .040±.003”.
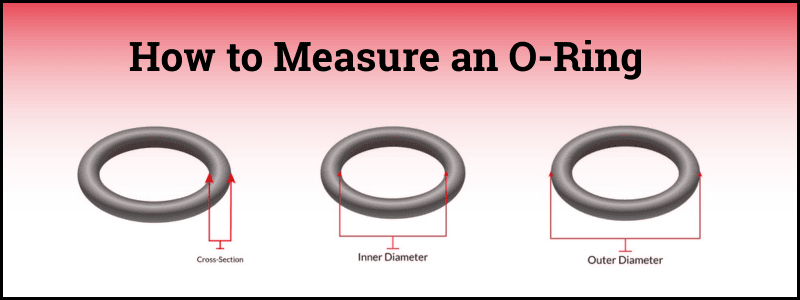
Tools for measuring O-rings include cones, calipers, and ring tapes. Measure ID across the center of the inside of the ring, and the thickness of the ring (CS). An o-ring’s outer diameter (OD) may also be helpful for identifying the correct size for an application, and this information is usually included in sizing charts. These formulas can help you determine all three values when some information is difficult to assess:
- Cross-Section (CS):The thickness of the O-ring.
𝐶𝑆=(𝑂𝐷−𝐼𝐷)÷2 - Inside Diameter (ID): The measurement across the hole in the center.
𝐼𝐷=𝑂𝐷−(𝐶𝑆×2) - Outside Diameter (OD): The measurement across the outer edge.
𝑂𝐷=𝐼𝐷+(𝐶𝑆×2)
Additional Tips for Working With O-Ring Charts
Many charts include values that are labeled as “actual” and “nominal.” Actual values refer to the true dimensions, such as .029” for ID and .040” for CS. Nominal values apply in name only, and represent how the sizes or values are described in words, such as a 1/32 nominal ID or 1/32 nominal CS. When measuring o-rings with calipers or another tool, always refer to the actual values to determine the size.